研究室工作进展 Jun. 3rd, 2015
Mechanistic Considerations of the Catalytic Guanylation Reaction of Amines with Carbodiimides for Guanidine Synthesis
Ling Xu, Wen-Xiong Zhang,* and Zhenfeng Xi
Organometallics 2015, 34, 1787−1801 (Review).
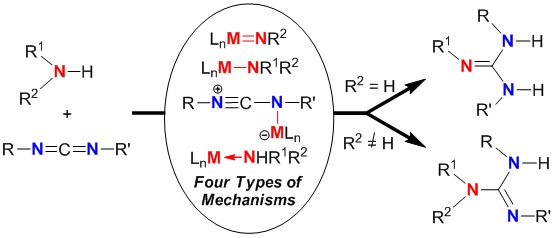
Catalytic guanylation reaction of amines with carbodiimides has received the increasing attention because of the atom-economical preparation of guanidines since 2003. To date, more than forty catalysts including transition metals, main group and rare-earth metals have been designed and tested for the guanylation reaction to construct acyclic and cyclic guanidines. In this review, we present a mechanistic consideration on catalytic guanylation reaction of amines with carbodiimides for guanidine synthesis to elucidate its development and importance. Four different types of reaction mechanisms are well categorized: [2+2]-cycloaddition/protonation mechanism, insertion/protonation mechanism, activation of carbodiimide/nucleophilic addition/intramolecular protonation mechanism, and protonation/nucleophilic addition/disassociation mechanism. It is useful to understand this reaction processes and accelerate the rapid development in the related area to meet the needs of the growing guanidines.
亮点介绍
胍作为一类重要的含氮有机化合物,是许多生物活性物质的结构单元,同时也作为碱性催化剂在有机合成中有广泛应用。胺对碳二亚胺的催化成胍(CGAC)反应,是一种直接的、原子经济性的方法制备胍。因该反应的原子经济性和胍的重要性,目前受到许多合成化学家和金属有机化学家的广泛关注。我们课题组在该领域做了系列的研究工作,例如: (1) 发现烷基铝,Zn(OTf)2和稀土金属催化剂等催化的高效合成胍的反应,并一锅法高效构筑了三氟甲基磺酸胍盐;(2) 通过肼分子中N-N键的断裂,实现了烷基锂催化的1,2-二芳基碳二亚胺的成胍反应构建胍;(3)无金属催化剂的条件下三组分反应构建环状胍。该系列成果发表在Organometallics 2009, 28, 882–887;Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 1816–1820;Organometallics 2011, 30, 5278–5283;Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 6266–6270(被OBC选为Cover Picture);Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 11941–11948;J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 12004–12009;Organometallics 2014, 33, 2784–2789;Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6274–6277;Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 254–265 ( Feature Article)。结合我们组和其他课题组的工作,从反应机理的角度详细阐释了该反应的发现,发展现状与重要性。
